# java stream 中 Collectors 的用法
-
java stream中Collectors的用法- 简介
-
Collectors.toList() -
Collectors.toSet() -
Collectors.toCollection() -
Collectors.toMap() -
Collectors.collectingAndThen() -
Collectors.joining() -
Collectors.counting() -
Collectors.summarizingDouble/Long/Int() -
Collectors.averagingDouble/Long/Int() -
Collectors.summingDouble/Long/Int() -
Collectors.maxBy()/minBy() -
Collectors.groupingBy() -
Collectors.partitioningBy()
# 简介
在 java stream 中,我们通常需要将处理后的 stream 转换成集合类,这个时候就需要用到 stream.collect 方法。 collect 方法需要传入一个 Collector 类型,要实现 Collector 还是很麻烦的,需要实现好几个接口。
于是 java 提供了更简单的 Collectors 工具类来方便我们构建 Collector 。
下面我们将会具体讲解 Collectors 的用法。
假如我们有这样两个 list:
1 | List<String> list = Arrays.asList("jack", "bob", "alice", "mark"); |
上面一个是无重复的 list ,一个是带重复数据的 list 。接下来的例子我们会用上面的两个 list 来讲解 Collectors 的用法。
# Collectors.toList()
1 | List<String> listResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList()); |

将 stream 转换为 list 。这里转换的 list 是 ArrayList ,如果想要转换成特定的 list ,需要使用 toCollection 方法。
# Collectors.toSet()
1 | Set<String> setResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()); |

# Collectors.toCollection()
上面的 toMap,toSet 转换出来的都是特定的类型,如果我们需要自定义,则可以使用 toCollection()
1 | List<String> custListResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)); |

# Collectors.toMap()
toMap 接收两个参数,第一个参数是 keyMapper ,第二个参数是 valueMapper :
1 | Map<String, Integer> mapResult = list.stream() |
如果 stream 中有重复的值,则转换会报 IllegalStateException 异常:
1 | Map<String, Integer> duplicateMapResult = duplicateList.stream() |
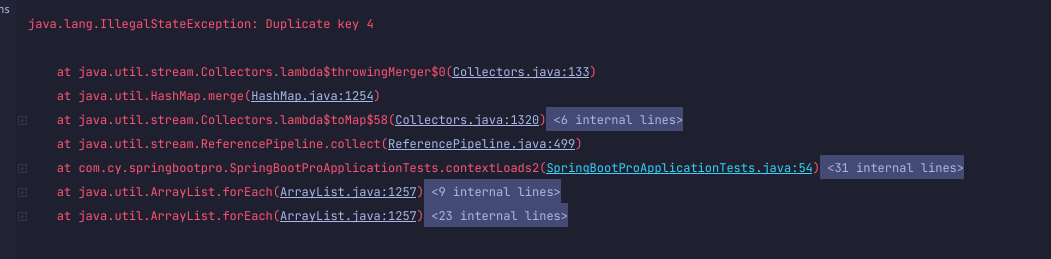
解决方案:
1 | Map<String, Integer> duplicateMapResult2 = duplicateList.stream() |
在 toMap 中添加第三个参数 mergeFunction ,来解决冲突的问题。

# Collectors.collectingAndThen()
collectingAndThen 允许我们对生成的集合再做一次操作。
1 | List<String> collectAndThenResult = list.stream() |

# Collectors.joining()
Joining 用来连接 stream 中的元素:
1 | String joinResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.joining()); |
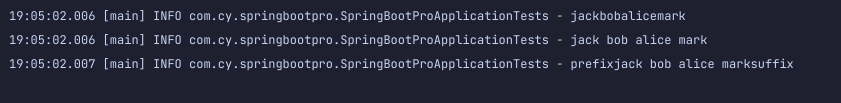
可以不带参数,也可以带一个参数,也可以带三个参数,根据我们的需要进行选择。
# Collectors.counting()
counting 主要用来统计 stream 中元素的个数:
1 | Long countResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.counting()); |

# Collectors.summarizingDouble/Long/Int()
SummarizingDouble/Long/Int 为 stream 中的元素生成了统计信息,返回的结果是一个统计类:
1 | IntSummaryStatistics intResult = list.stream() |

# Collectors.averagingDouble/Long/Int()
averagingDouble/Long/Int() 对 stream 中的元素做平均:
1 | Double averageResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(String::length)); |

# Collectors.summingDouble/Long/Int()
summingDouble/Long/Int() 对 stream 中的元素做 sum 操作:
1 | Double summingResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summingDouble(String::length)); |

# Collectors.maxBy()/minBy()
maxBy()/minBy() 根据提供的 Comparator ,返回 stream 中的最大或者最小值:
1 | Optional<String> maxByResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.naturalOrder())); |

# Collectors.groupingBy()
GroupingBy 根据某些属性进行分组,并返回一个 Map :
1 | Map<Integer, Set<String>> groupByResult = list.stream() |

# Collectors.partitioningBy()
PartitioningBy 是一个特别的 groupingBy,PartitioningBy 返回一个 Map ,这个 Map 是以 boolean 值为 key ,从而将 stream 分成两部分,一部分是匹配 PartitioningBy 条件的,一部分是不满足条件的:
